|
Q. 1 – Q. 20 carry one mark each.
|
|
1.
|
If a complex
variable z = 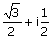 ,
then z4 is ,
then z4 is
(A) 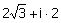
(B) 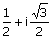
(C) 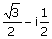
(D) 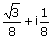
|
|
2.
|
Two cards are
drawn at random in succession, with replacement, from a deck of 52 well
shuffled cards. Probability of getting both 'Aces' is
(A) 1/169
(B) 2/169
(C) 1/13
(D) 2/13
|
|
3.
|
The angle (in
degrees) between two planar vectors 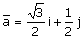 and and
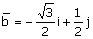
(A) 30
(B) 60
(C) 90
(D) 120
|
|
4.
|
What is the
value of 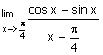
(A) 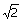
(B) 0
(C) 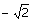
(D) Limit
does not exist
|
|
5.
|
The
determinant 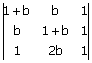 evaluates
to evaluates
to
(A) 0
(B) 2b(b-1)
(C) 2(1-b)(1+b)
(D) 3b(1+b)
|
|
6.
|
¦(x) = |x| is a function defined for real
numbers x. The directional derivative of ¦
at x=o in the direction d = -1 is
(A) 1
(B) 0
(C) -1/2
(D) -1
|
|
7.
|
Which one of
the following planar mechanisms does NOT provide quick-return motion?
(A) Scotch-Yoke
(B) Whitworth
(C) Off-set
slider crank
(D) Drag
link
|
|
8.
|
The geometric
tolerance that does NOT need a datum for its specification is
(A) Concentricity
(B) Runout
(C) Perpendicularity
(D) Flatness
|
|
9.
|
Oil in
hydraulic cylinder is compressed from an initial volume of 2 m3 to 1.96 m3. If the pressure of oil in the
cylinder changes from 40 MPa to 80 MPa during compression, the bulk modules
of elasticity of oil is
(A) 1000
MPa
(B) 2000
MPa
(C) 4000
MPa
(D) 8000
MPa
|
|
10.
|
A component
made of material with modulus of elasticity of 200 MPa and modulus of
rigidity of 80 MPa experience an axial strain of 1000. The lateral strain
experienced by the component within the elastic limit is
(A) 250
(B) 400
(C) 500
(D) 800
|
|
11.
|
Which one of
the following cooling methods is best suited for converting Austenite steel
into very fine Pearlite steel?
(A) Oil
quenching
(B) Water
quenching
(C) Air
cooling
(D) Furnace
cooling
|
|
12.
|
Reaming is
primarily used for achieving
(A) Higher
MRR
(B) Improved
dimensional tolerance
(C) fine
surface finish
(D) Improved
positional tolerance
|
|
13.
|
The
interpolator in a CNC machine controls
(A) Spindle
speed
(B) Coolant
flow
(C) Feed
rate
(D) Tool
change
|
|
14.
|
Which one of
the following instruments is a comparator?
(A) Tool
Maker's Microscope
(B) Go/No
Go gage
(C) Optical
Interferometer
(D) Dial
Gauge
|
|
15.
|
Which one of
the following is an indispensable part of just-in-Time manufacturing of
multiple products on a line?
(A) Outbound
quality inspection
(B) Lot sizing
(C) Safety
stocks
(D) Set
up time reduction
|
|
16.
|
During an
economic analysis of a capital investment proposal, the cost that can be
ignored is
(A) Sunk
cost
(B) Fixed
cost
(C) Marginal
cost
(D) Variable
cost
|
|
17.
|
Which one of
the following is an effective therblig?
(A) Position
(B) Inspect
(C) Grasp
(D) Search
|
|
18.
|
In queueing
models, M/M/c denotes a Poisson arrival process and
(A) exponentially
distributed service times and c servers in series
(B) constant
service times and c servers in series
(C) exponentially
distributed service times and c serves in parallel
(D) constant
service times and c servers in parallel
|
|
19.
|
A product is
made by mixing three raw materials 1, 2, 3 in varying proportions, where
material 1 must account for not more than 50% of the total. If x, y and z are
the amounts of raw materials 1, 2, and 3 respectively, this constrain can be
modeled as
(A) x £ 0.5
(B) x £ 0.5(x + y + z)
(C) 0.5x
£ x + y + z
(D) x ³ 0.5(y + z)
|
|
20.
|
Which one of
the following cost components is a part of appraisal costs related to
quality?
(A) Quality
planning and engineering cost
(B) Process
control cost
(C) Quality
data acquisition and analysis cost
(D) Product
inspection and testing cost
|
|
|
Q. 21 to Q.
75 carry two marks each.
|
|
21.
|
If X is a
continuous random variable whose probability density function is given by
¦(x) = 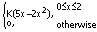
Then P(X>1)
is:
(A) 3/14
(B) 4/5
(C) 14/17
(D) 17/28
|
|
22.
|
The random
variable X takes on the values 1, 2 or 3 with probabilities(2+5p)/5,
(1+3p)/5, and (1.5_2p)/5, respectively. The values of P and E[X] are respectively
(A) 0.05,
1.87
(B) 1.90,
5.87
(C) 0.05,
1.10
(D) 0.25,
1.40
|
|
23.
|
If A is square
symmetric real valued matrix of dimension 2n, the eigenvalues of A are
(A) 2n
distinct real values
(B) 2n
real values, not necessarily distinct
(C) n
distinct pairs of complex conjugate numbers
(D) n
pairs of complex conjugate numbers, not necessarily distinct
|
|
24.
|
The function ex over the interval [0,1] is to be
evaluated using the Taylor series 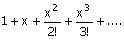 to
an accuracy of d > 0. The number
of terms in the series that is considered for this accuracy is n. Then to
an accuracy of d > 0. The number
of terms in the series that is considered for this accuracy is n. Then
(A) for
a given x Î [0, 1] and a given d, there is no finite n that is valid
(B) for
a given d > 0, there is valid n
that is finite for a given x Î [0,
1], but there is no finite n that is valid for all x Î [0, 1]
(C) for
a given d > 0, there is a finite n
that is valid for all x Î [0, 1]
(D) there
is a finite n that is valid for all x in [0, 1] and all d > 0
|
|
25.
|
For the
function ¦(x, y) = x2 -
y2 defined on R2, the point [0,0] is
(A) a
local minimum
(B) a
local maximum
(C) neither
a local minimum nor a local maximum
(D) both
a local minimum and a local maximum
|
|
26.
|
ql,….qm
are n-dimensional vectors, with m < n. This set of vectors is linearly
dependent. Q is the matrix with ql,….qm as the columns.
The rank of Q is
(A) Less
than m
(B) m
(C) Between
m and n
(D) n
|
|
27.
|
"Matching
Exercise". Choose the correct one out of the alternatives A, B, C, D.
|
Group 1
|
Group 2
|
|
P – Second
order differential equations
|
1 –
Runge-Kutta method
|
|
Q –
Nonlinear algebraic equations
|
2 –
Newton-Raphson method
|
|
R – Linear
algebraic equations
|
3 – Gauss
elimination
|
|
S –
Numerical integration
|
4 –
Simpson's rule
|
(A) P-3,
Q-2, R-4, S-1
(B) P-2,
Q-4, R-3, S-1
(C) P-1,
Q-2, R-3, S-4
(D) P-1,
Q-3, R-2, S-4
|
|
28.
|
A disc type
fly wheel having a mass of 10 kg and radius 0.2 m is replaced in a single
cylinder engine by a system of dynamically equivalent concentrated masses m1
and m2 rotating about the flywheel axis as shown below. If the
distance x1 is 0.1 m then the distance x2 is
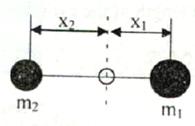
(A) 0.1
m
(B) 0.2
m
(C) 0.4
m
(D) 0.8
m
|
|
29.
|
A radial disc
cam rotating at a constant speed of 60 rpm provides a parabolic displacement
of 0.2 m to its flat faced rectilinear follower during 90° of its rotation. The acceleration (m/s2) experienced by the follower is
(A) 0.8
(B) 1.6
(C) 3.2
(D) 6.4
|
|
30.
|
Figure below
shows a mass of 300 kg being pushed using a cylindrical rod made of a
material having E = 22 MPa and of 2 m length and 0.1 m in diameter. In order
to avoid the failure of the rod due to elastic instability, the maximum value
of the coefficient of Coulomb friction permissible between the mass and floor
is
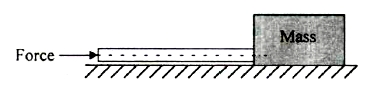
(A) 0.22
(B) 0.36
(C) 0.65
(D) 0.75
|
|
31.
|
A cylindrical
tank is filled with water as shown in the Figure below. The force required to
close the discharge tube at the bottom of the tank is
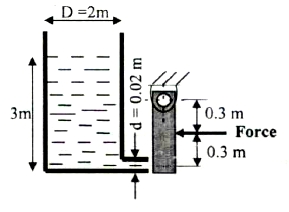
(A) 18.5
N
(B) 37
N
(C) 45.5
N
(D) 74
N
|
|
32.
|
When an ideal
gas (Cp = 3.5) is heated at constant pressure from 25°C to 425°C,
the change in entropy is
(A) 1.48
(B) 2.97
(C) 4.2
(D) 5.98
|
|
33.
|
A long glass
cylinder of inner diameter = 0.03 m and outer diameter = 0.05 m carries hot
fluid inside. If the thermal conductivity of glass = 1.05 W/mK, the thermal
resistance (°K/W) per unit length of
the cylinder is
(A) 0.031
(B) 0.077
(C) 0.17
(D) 0.34
|
|
34.
|
A tool with
side Cutting Edge angle of 30° and
Edge angle of 10° is used for fine
turning with a feed of 1 mm/rev. Neglecting nose radius of the tool, the
maximum (peak to valley) height of surface roughness produced will be
(A) 0.16
mm
(B) 0.26
mm
(C) 0.32
mm
(D) 0.48
mm
|
|
35.
|
Which one of
the following process conditions leads to higher MRR in ECM process?
(A) higher
current, larger atomic weight
(B) higher
valency, lower current
(C) lower
atomic weight, lower valency
(D) higher
valency, lower atomic weight
|
|
36.
|
In an Abrasive
jet machining process, if Q = flow rate of the abrasives and d = the mean
diameter of the abrasive grain, then material removal rate is proportional to
(A) Q/d2
(B) Qd
(C) Qd2
(D) Qd3
|
|
37.
|
"Matching
Exercise". Choose the correct one out of the alternatives A, B, C, D.
|
Group
|
Group 2
|
|
P – Plastic
Carry-bags
|
1 –
Thermo-Vacuum Forming
|
|
Q – O-rings
|
2 – Blow
Molding
|
|
R – Shrink
Wrappers
|
3 –
Compression Molding
|
|
S –
Automobile Dashboards
|
4 – Resin
Transfer Molding
|
(A) P-2,
Q-3, R-1, S-4
(B) P-1,
Q-2, R-3, S-4
(C) P-3,
Q-4, R-1, S-2
(D) P-2,
Q-3, R-4, S-1
|
|
38.
|
"Matching
Exercise". Choose the correct one out of the alternatives A, B, C, D.
|
Group 1
|
Group 2
|
|
P – Sand
Casting
|
1 – Turbine
blades
|
|
Q –
Centrifugal Casting
|
2 – I.C.
Engine pistons
|
|
R –
Investment Casting
|
3 – Large
bells
|
|
S – Die
casting
|
4 –
Pulllllleys
|
(A) P-4,
Q-1, R-3, S-2
(B) P-2,
Q-4, R-3, S-1
(C) P-1,
Q-4, R-1, S-2
(D) P-3,
Q-2, R-1, S-4
|
|
39.
|
Tolerance on
the dimension x in the two component assembly shown below i 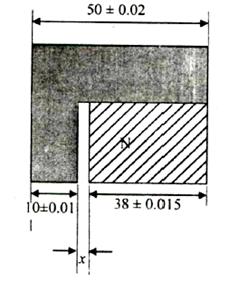
(A) ± 0.025
(B) ± 0.030
(C) ± 0.040
(D) ± 0.045
|
|
40
|
The maximum
possible percentage reduction in area per pass during wire drawing of an
ideal plastic material without friction is of the order of
(A) 37
(B) 50
(C) 63
(D) 75
|
|
41.
|
Circular
blanks of 35 mm diameter are punched from a steel sheet of 2 mm thickness. If
the clearance per side between the punch and die is to be kept as 40 microns,
the sizes of punch and die should respectively be (A) 35+0.00 and 35+0.040
(B) 35-0.040 and 35-0.080
(C) 35+0.00 and 35+0.080
(D) 35+0.040 and 35-0.080
|
|
42.
|
In a CAD
package, a point P (6, 3, 2) is projected along a vector v (-2, 1, -1).
The projection of this point on X-Y plane will be
(A) (4,
4, 0)
(B) (8,
2, 0)
(C) (7,
4, 0)
(D) (2,
5, 0)
|
|
43.
|
The geometric
transformation specified by [x¢ y¢ 1] = [x y 1]  in
a 2 D CAD system represents in
a 2 D CAD system represents
(A) Scaling
and Translation
(B) Scaling
and Rotation
(C) Rotation
and Translation
(D) Rotation
|
|
44.
|
The figure
below shows the cross-section of circular fillet weld joining a cylindrical
steel pin to a steel plate. If the pin is subjected to pure torsional load,
the shear stress (MPa) occurring at the throat of the weld is
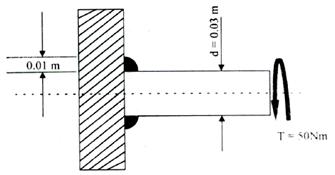
(A) 2.5
(B) 5.0
(C) 7.0
(D) 10
|
|
45.
|
Diameter of a
hole after plating needs to be controlled between 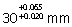 .
If the plating thickness varies between 10-15 microns, diameter of the hole
before plating should be .
If the plating thickness varies between 10-15 microns, diameter of the hole
before plating should be
(A) 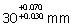
(B) 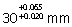
(C) 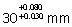
(D) 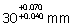
|
|
46.
|
The D.C. power
source for are welding has the characteristic 3V + 1 = 240, where V = Voltage
and 1 = Current in amp. For maximum arc power at the electrode, voltage
should be set at
(A) 20
V
(B) 40
V
(C) 60
V
(D) 80
V
|
|
47.
|
In a CNC
machine feed drive, a stepper motor with step angle of 1.80 drives a lead screw with pitch of
2 mm. The Basic Length Unit (BLU) for this drive is
(A) 10
microns
(B) 20
microns
(C) 40
microns
(D) 100
microns
|
|
48.
|
Which one of
the following gear manufacturing processes is NOT based on
(A) Gear
Hobbing
(B) Gear
Shaping
(C) Gear
Milling
(D) Gear
Shaving
|
|
49.
|
Based on the
general characteristics of the different types of layout, which of the
following are true?
P -
Work-in-process and throughput time are high in process layout
Q - Production
cost per unit is high in product layout
R -
Work-in-process and throughput time are high in product layout
(A) P
and Q
(B) Q
and R
(C) Only
P
(D) Only
R
|
|
50.
|
In sensitivity
analysis of LP models, which of the following holds true?
P – Reduced
cost of basic variables are zero at optimality
Q –
Constraints are binding when shadow prices are non-zero
R –
Constraints are binding when shadow prices are zero
S – Reduced
cost is same as shadow price
(A) P
and Q
(B) Q
and R
(C) P
and R
(D) Q
and S
|
|
51.
|
Consider the
symmetric dual pair of LPs [P] and [D], where A is an m ´ n matrix, b is an m-vector and c is an
n-vector
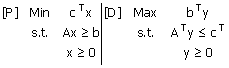
Assuming that
[P] is feasible. If the optimal values are 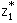 for
[P] and for
[P] and 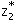 for
[D], whenever they exist, then which one of the following is true? for
[D], whenever they exist, then which one of the following is true?
(A) If
[D] is infeasible, then 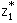 can be determined and is equal to
can be determined and is equal to 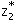
(B) If
[D] is feasible, then 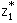 cannot
be determined cannot
be determined
(C) If
[D] is feasible, then 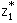 can
be determined and is equal to can
be determined and is equal to 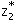
(D) If
[D] is feasible, then 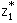 can
be determined but not equal to can
be determined but not equal to 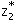
|
|
52.
|
The moving
average method is to be used for forecasting demand based on m periods of
data. Two values of m are tried, m1 and m2 with m1
> m2, to get two different forecasts, denoted by F(t) and G(t).
P = F(t) has
less variability than G(t)
Q – Forecast
error of F(t) is less than that of G(t)
Which of the
above statements are true?
(A) Only
P
(B) Only
Q
(C) Both
P and Q
(D) Neither
P nor Q
|
|
53.
|
In an
optimization problem, let y be a 0 – 1 variable and x be a positive real
number. Now, the condition that x can take non-zero values only if y = 1 can
be modeled using the linear constraint
(A) x £ My (M is a large number)
(B) x ³
y
(C) x ³ My (M is a large number)
(D) xy ³ 0
|
|
54.
|
The average
number of accidents occurring monthly on an assembly shop floor is 2. The
probability that there will be at least one accident in this month is
estimated to be
(A) 0.055
(B) 0.456
(C) 0.865
(D) 0.950
|
|
55.
|
X1,
… , X100 are Bernoulli random variables with a probability of
success equal to 0.6. By the Central Limited Theorem, the random variable Y =
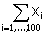 is
approximately normally distributed. Then Y has mean and variance respectively
equal to is
approximately normally distributed. Then Y has mean and variance respectively
equal to
(A) 40
and 24
(B) 60
and 24
(C) 40
and 12
(D) 60
and 12
|
|
56.
|
Karmarkar's
algorithm for Linear Programming
(A) moves
along different extreme point solutions of the feasible region
(B) enumerates
all possible extreme point solutions
(C) divides
the feasible region into different parts for function evaluation
(D) generates
interior point iterates which converges to the optimum solution
|
|
57.
|
For a
transportation problem that has a feasible solution, the northwest corner
rule gives a possible solution which is
(A) a
basic feasible solution to the problem
(B) a
near optimal solution to the problem
(C) the
optimal solution to the problem
(D) one
of the many optimal solution to the problem
|
|
58.
|
The assignment
problem in Linear Programming is also an example of a discrete optimization
problem. How many feasible solutions are there to this problem defined on n
jobs and n persons?
(A) nn
(B) n(n-1)
(C) n2
(D) n!
|
|
59.
|
"Matching
Exercise". Choose the correct one out of the alternatives A, B, C, D.
|
Group 1
|
Group 2
|
|
P –
Knowledge Based System
|
1 – responds
to queries with reports
|
|
Q – Decision
Support System
|
2 – uses
statistical rules of inference
|
|
R –
Management Information System
|
3 – provides
recommendations
|
|
S – Data
Mining
|
4 – uses
reasoning techniques
|
(A) P-4,
Q-3, R-1, S-2
(B) P-2,
Q-3, R-1, S-4
(C) P-4,
Q-2, R-3, S-1
(D) P-1,
Q-4, R-1, S-2
|
|
60.
|
A process is
to be controlled with standard values m
= 15 and s = 3.6. The sample size is
9. The controls limits for the 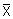 chart
are chart
are
(A) 15 ± 10.8
(B) 15 ± 3.6
(C) 0.4
± 10.8
(D) 0.4
± 3.6
|
|
61.
|
Item p is made
from components Q and R. Item Q, in turn, is made from S and T. The lead
times for items P, Q, R, S, and T are 2, 3, 10, 5, and 6 weeks, respectively.
The lead time (in weeks) needed to respond to a customer order for item P
is
(A) 10
(B) 11
(C) 12
(D) 26
|
|
62.
|
The
reliability of an equipment for a time t failure exceeding t is given by R
(t) = exp(-lt). The mean time to failure (MTTF) for this equipment (in
hours) is
(A) l
(B) 1/l
(C) (1/l2)
(D) l2
|
|
63.
|
Four jobs have
to be sequenced on a single facility, with the objective of minimizing the
maximum tardiness (=max; |Completion time; - Due date;|). The jobs have due
dates and processing times as follows
|
Job
|
Due date
(day number)
|
Processing
time (days)
|
|
P
|
5
|
2
|
|
Q
|
6
|
10
|
|
R
|
3
|
3
|
|
S
|
7
|
4
|
The
last job that should be taken up is
(A) P
(B) Q
(C) R
(D) S
|
|
64.
|
An asset
investment is made for Rs. 1,20,000. The uniform costs per year are Rs.
40,000 in operating the asset. Uniform benefits per year are either Rs.
60,000 or Rs. 80,000. Judged to be equally likely. What is the expected
payback period?
(A) 3
(B) 4.5
(C) 6
(D) 9
|
|
65.
|
|
Activity
|
Time (minutes)
|
|
Machine
loading + unloading
|
2
|
|
Machining
|
4
|
|
Walking from
one machine to the next
|
1
|
For the data
given above, how many machines can be assigned to an operator to minimize
idle time of the operator and machines?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
|
|
66.
|
Given
Assertion
[a]: Value engineering of a new product is to be done after the original
design concept is nearly ready for release for manufacture
Reason [r]: Value
engineering aims at reducing the cost of manufacture of a new product
(A) Both
[a] and [r] are true and [r] is the correct reason for [a]
(B) Both
[a] and [r] are true, but [r] is not the correct reason for [a]
(C) Both
[a] and [r] are false
(D) [a]
is true but [r] is false
|
|
67.
|
Given
Assertion
[a]: There is a continuous reduction of life cycles of modern day
products
Reason [r]:
Product life cycle management reduces to a large extent the new product
development time from concept to production
(A) Both
[a] and [r] are true and [r] is the correct reason for [a]
(B) Both
[a] and [r] are true, but [r] is not the correct reason for [a]
(C) Both
[a] and [r] are false
(D) [a]
is true but [r] is false
|
|
68.
|
The problem of
finding the rectangle of maximum area with perimeter equal to 20 can be posed
as the constrained optimization problem
Max xy
s.t
2x + 2y = 20
x, y ³ 0
The solution
to this problem is x = y = 5. What is the value of the Lagrange multiplier
corresponding to the perimeter constraint?
(A) 2.5
(B) 5
(C) 7.5
(D) 10
|
|
69.
|
A
manufacturing system with a production rate p units/day experiences a demand
rate of d units/dsy where P > d. Let Q be the maximum production quantity
per period. When the total production in a period reaches Q units, the
production is stopped and restarted only when inventory becomes zero. In such
a scenario, the maximum cycle inventory is
(A) 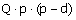
(B) 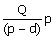
(C) 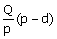
(D) ww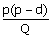
|
|
70.
|
In a time
study, the observed times and ratings for an elemental operation are as shown
below:
|
|
Reading 1
|
Reading 2
|
|
Rating (%)
|
80
|
100
|
|
Observed
time (minutes)
|
0.60
|
0.50
|
Considering an
allowance of 10% of the normal time, the standard time (in minutes) for the
operations is
(A) 0.49
(B) 0.54
(C) 0.98
(D) 1.08
|
|
|
Common Data
Questions
|
|
|
Common Data
for Questions 71, 72, 73:
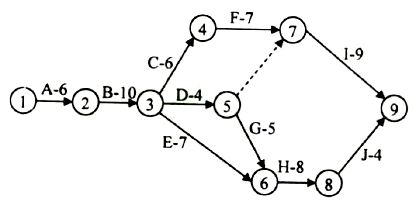
The figure
below illustrates a project network describing the precedence relationships
among different
activities
(A-J). The activities along with their duration in weeks are represented as
arcs, and the events are
shown as nodes
(1 is the start event and 9 is the end event).
|
|
71.
|
The length of
critical path in weeks is
(A) 29
(B) 31
(C) 38
(D) 66
|
|
72.
|
If Ua is the earliest start time of
eventa, then the recurrence equation
defining U6 is
(A) U6
= Max {U8, 8}
(B) U6
= U8 - 8
(C) U6
= Max {U3, U5, 7, 5}
(D) U6
= Max {U3 + 7, U5 + 5}
|
|
73.
|
If activity B
has uncertain duration and is uniformly distributed over the interval [8,
12], and T is the earliest start time of event 3 (assume that event 1 starts
at time 0), then the mean and variance of T are
(A) 10
and 0.4
(B) 10
and 1.33
(C) 16
and 0.4
(D) 16
and 1.33
|
|
|
Common Data
for Questions 74, 75:
In an
orthogonal machining test, the following observations were made
|
Cutting
force
|
1200 N
|
|
Thrust force
|
500 N
|
|
Tool rake
angle
|
Zero
|
|
Cutting
speed
|
1 m/s
|
|
Depth of cut
|
0.8 mm
|
|
Chip
thickness
|
1.5 mm
|
|
|
74.
|
Friction angle
during machining will be
(A) 22.6°
(B) 32.8°
(C) 57.1°
(D) 67.4°
|
|
75.
|
Chip speed
along the tool rake face will be
(A) 0.83
m/s
(B) 0.53
m/s
(C) 1.2
m/s
(D) 1.88
m/s
|
|
|
Linked
Answer Questions: Q.76 to Q.85 carry two marks each.
|
|
|
Statement
for Linked Answer Questions 76 &
77:
In the setup
shown below, 2k W power is supplied by oil flowing into the cylinder of the
hydraulic actuator at the rate of 400 ´
10-6 m3/s.
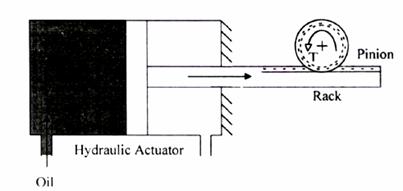
|
|
76.
|
If the
diameter of the piston is 0.05 m, the force (kN) generated on the piston is
(A) 1.6
(B) 4.8
(C) 9.8
(D) 12.2
|
|
77.
|
The pinion is
a spur gear having 30 teeth of 2 mm module. The torque T (Nm) generated is
(A) 36
(B) 72
(C) 147
(D) 294
|
|
|
Statement
for Linked Answer Questions 78 &
79:
Consider an
unbalanced serial assembly line consisting o three workstations that produces
a single pare. The part visits each workstation exactly once. The number of
parallel machines at each workstation and the processing time at a machine is
shown below:
|
Workstation
|
Number of
machines
|
Processing
time (minutes)
|
|
1
|
1
|
2
|
|
2
|
2
|
5
|
|
3
|
6
|
10
|
|
|
78.
|
What is the
capacity (in parts/minute) of the above assembly line?
(A) 0.1
(B) 0.4
(C) 0.5
(D) 0.6
|
|
79.
|
The minimum WIP
level that allows the line to operate under maximum capacity is
(A) 1.7
(B) 4.0
(C) 6.8
(D) 8.6
|
|
|
Statement
for Linked Answer Questions 80 &
81:
Blind holes 10
mm diameter, 50 mm deep are being drilled in steel block. Drilling spindle
speed is 600 rpm, feed 0.2 mm/rev, point angle of drill is 120°.
|
|
80.
|
Machining time
(in minutes ) per hole will be
(A) 0.08
(B) 0.31
(C) 0.44
(D) 0.86
|
|
81.
|
During the
above operation, the drill wears out after producing 200 holes. Taylor's tool life equation is of the form VT0.3
= C, where V = cutting speed in m/minute and T = tool life in minutes. Taylor's constant C will be
(A) 15
(B) 72
(C) 93
(D) 490
|
|
|
Statement
for Linked Answer Questions 82&
83:
A company
manufactures light bulbs using a production process that yields bulbs with an
average life of 1000 hours, 1300 hours, and 900 hours respectively.
|
|
82.
|
The process
capability index (CPK) for the manufacturing process is
(A) 0.67
(B) 1.00
(C) 1.33
(D) 2.00
|
|
83.
|
For the above
manufacturing process, the ratio of the potential process capability to its
actual process capability is
(A) 0.50
(B) 0.67
(C) 1.00
(D) 2.00
|
|
|
Statement
for Linked Answer Questions 84 &
85:
In a sand
casting process, a sprue of 10 mm base diameter and 250 mm height leads to a
runner which fills a cubical mould cavity of 100 mm size
|
|
84.
|
The volume
flow rate (in mm3 /s) is
(A) 0.8
´ 105
(B) 1.1
´ 105
(C) 1.7
´ 105
(D) 2.3
´ 105
|
|
85.
|
The mould
filling time (in seconds) is
(A) 2.8
(B) 5.78
(C) 7.54
(D) 8.41
|
|
|
END OF THE
QUESTION PAPER
|