GATE 2009 Mechanical Engineering Question PaperQ. No. 1 – 20 Carry One Mark Each
1. For a matrix [M]=
(A) - (B) - (C) (D)
2. The divergence of the
vector field (A) 7 (B) 4 (C) 3 (D) 0
3. The inverse Laplace transform of (A) 1 + et (B) 1 - et (C) 1 - e-t (D) 1 + et
4. If three coins are tossed simultaneously, the probability of getting at least one head (A) 1/8 (B) 3/8 (C) 1/2 (D) 7/8
5. If a closed system is undergoing an irreversible process, the entropy of the system (A) Must increase (B) Always remains constant (C) Must decrease (D) Can increase, decrease or remain constant
6. A coolant fluid at 30°C flows over a heated flat plate maintained at a constant temperature of 100°C. The boundary layer temperature distribution at a given location on the plate may be approximated as T = 30 + 70 exp (-y) where y (in m) is the distance normal to the plate and T is in °C. If thermal conductivity of the fluid is 1.0W/mK, the local convective heat transfer coefficient (in W/m2K) at that location will be (A) 0.2 (B) 1 (C) 5 (D) 10
7. A frictionless piston-cylinder device contains a gas initially at 0.8MPa and 0.015 m3. It expands quasi-statically at constant temperature to a final volume of 0.030 m3. The work output (in kJ) during this process will be (A) 8.32 (B) 12.00 (C) 554.67 (D) 8320.00
8. In an ideal vapour compression refrigeration cycle, the specific enthalpy of refrigerant (in kJ/kg) at the following states is given as: Inlet of condenser: 283 Exit of condenser: 116 Exit of evaporator: 232 The COP of this cycle is (A) 2.27 (B) 2.75 (C) 3.27 (D) 3.75
9. A compressor undergoes a reversible, steady flow process. The gas at inlet and outlet of the compressor is designated as state 1 and state 2 respectively. Potential and kinetic energy changes are to be ignored. The following notations are used: v= specific volume and P=pressure of the gas. The specific work required to be supplied to the compressor for this gas compression process is (A) (B) (C) v1 (P2 - P1) (D) -P2 (v1 - v2)
10. A block weighing 981N is resting on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the block and the horizontal surface is m = 0.2A vertical cable attached to the block provides partial support as shown. A man can pull horizontally with a force of 100N. What will be the tension, T (in N) in the cable if the man is just able to move the block to the right?
(A) 176.2 (B) 196.0 (C) 481.0 (D) 981.0
11. If the principal stresses in a plane stress problem, are s1 = 100MPa, s2 = 40MPa, the magnitude of the maximum shear stress (in MPa) will be (A) 60 (B) 50 (C) 30 (D) 20
12. A simple quick return mechanism is shown in the figure. The forward to return ratio of the quick return mechanism is 2:1. If the radius of the crank O1P is 125 mm, then the distance 'd' (in mm) between the crank centre to lever pivot centre point should be
(A) 144.3 (B) 216.5 (C) 240.0 (D) 250.0
13. The rotor shaft of a large electric motor supported between short bearings at both deflection of 1.8mm in the middle of the rotor. Assuming the rotor to be perfectly balanced and supported at knife edges at both the ends, the likely critical speed (in rpm) of the shaft is (A) 350 (B) 705 (C) 2810 (D) 4430
14. A solid circular shaft of diameter d is subjected
to a combined bending moment M and torque, T. The material property to be used
for designing the shaft using the relation (A) ultimate tensile strength (Su) (B) tensile yield strength (Sy) (C) torsional yield strength (Ssy) (D) endurance strength (Se)
15. The effective number of lattice points in the unit cell of simple cubic, body centered cubic, and face centered cubic space lattices, respectively, are (A) 1,2,2 (B) 1,2,4 (C) 2,3,4 (D) 2,4,4
16. Friction at the tool-chip interface can be reduced by (A) decreasing the rake angle (B) increasing the depth of cut (C) decreasing the cutting speed (D) increasing the cutting speed
17. Two streams of liquid metal, which are not hot enough to fuse properly, result into a casting defect known as (A) cold shut (B) swell (C) sand wash (D) scab
18. The expected time (te) of a PERT activity in terms of optimistic time (t0), pessimistic time (tp) and most likely time (tl) is given by (A) (C) (C) (D)
19. Which of the following is the correct data structure for solid models? (A) solid part ® faces ® edges ® vertices (B) solid part ® edges ® faces ® vertices (C) vertices ® edges _ faces ® solid parts (D) vertices ® faces ® edges ® solid parts
20. Which of the following forecasting methods takes a fraction of forecast error into account for the next period forecast? (A) simple average method (B) moving average method (C) weighted moving average method (D) exponential smoothening method
Q. No. 21 – 56 Carry Two Marks Each
21. An analytic function of a complex variable z = x + iy is expressed as
f(z) = u (x, y) + iv (x,
y) where I =
(A) (B) (C) (D)
22. The solution of x (A) y = (B) (C) y = (D) y =
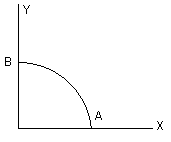
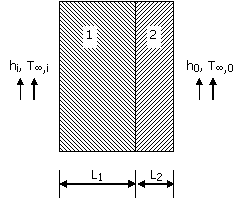
23. A path AB in the form of one quarter of a circle of unit radius is shown in the figure. Integration of (x +y)2 on path AB traversed in a counter-clockwise sense is
(A) (B) (C) (D) 1
24. The distance between the origin and the point nearest to it on the surface z2 = 1 + xy is (A) 1 (B) (C) (D) 2
25. The area enclosed between the curves y2 = 4x and x2 = 4y is (A) (B) 8 (C) (D) 16
26. The standard deviation of a uniformly distributed random variable between 0 and 1 is (A) (B) (C) (D)
27. Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe where the diameter is reduced from 20cm to 10cm. The pressure in the 20cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150kPa. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50kPa and a specific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3/s) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation is (A) 0.05 (B) 0.16 (C) 0.27 (D) 0.38
28. In a parallel flow heat exchanger operating under steady state, the heat capacity rates (product of specific heat at constant pressure and mass flow rate) of the hot and cold fluid are equal. The hot fluid, flowing at 1kg/s with Cp = 4kJ/kgK, enters the heat exchanger at 102°C while the cold fluid has an inlet temperature of 15°C. The overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger is estimated to be 1kW/m2K and the corresponding heat transfer surface area is 5m2. Neglect heat transfer between the heat exchanger and the ambient. The heat exchanger is characterized by the following relation: 2e = 1 − exp (−2NTU). The exit temperature (in °C) for the cold fluid is (A) 45 (B) 55 (C) 65 (D) 75
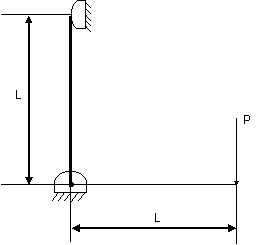
29. In an air-standard Otto cycle, the compression ratio is 10. The condition at the beginning of the compression process is 100kPa and 27°C. Heat added at constant volume is 1500kJ/kg, while 700kJ/kg of heat is rejected during the other constant volume process in the cycle. Specific gas constant for air=0.287 kJ/kgK. The mean effective pressure (in kPa) of the cycle is (A) 103 (B) 310 (C) 515 (D) 1032
30. An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50kW. The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is (A) 50 (B) 250 (C) 300 (D) 360
31. You are asked to evaluate assorted fluid flows for their suitability in a given laboratory application. The following three flow choices, expressed in terms of the two-dimensional velocity fields in the xy-plane, are made available. P. u = 2y, v = -3x Q. u = 3xy, v = 0 R. u = -2x, v = 2y Which flow(s) should be recommended when the application requires the flow to be incompressible and irrotational? (A) P and R (B) Q (C) Q and R (D) R
32. Water at 25°C is flowing through a 1.0km long G.I pipe of 200mm diameter at the rate of 0.07m3/s. If value of Darcy friction factor for this pipe is 0.02 and density of water is 1000kg/m3, the pumping power (in kW) required to maintain the flow is (A) 1.8 (B) 17.4 (C) 20.5 (D) 41.0
33. Consider steady-state heat conduction across the thickness in a plane composite wall (as shown in the figure) exposed to convection conditions on both sides.
Given: Hi = 20W / m2K; h0 = 50W / m2K; T¥,i = 20°C; T¥,0 = -2°C; k1 = 20W / mK; k2 = 50W / mK; L1 = 0.30m and L2 = 0.15m.
Assuming negligible contact resistance between the
wall surfaces, the interface temperature, (A) -0.50 (B) 2.75 (C) 3.75 (D) 4.50
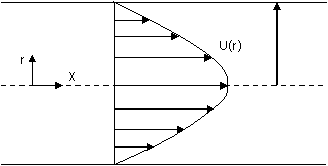
34. The velocity profile of a fully developed laminar
flow in a straight circular pipe, as shown in the figure, is given by the
expression u(r) = -
(A) - (B) - (C) - (D) -
35. A solid shaft of diameter, d and length L is fixed at both the ends. A torque, T0 is applied at a distance, L/4 from the left end as shown in the figure given below.
The maximum shear stress in the shaft is
(A) (B) (C) (D)
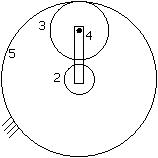
36. An epicyclic gear train is shown schematically in the adjacent figure The sun gear 2 on the input shaft is a 20 teeth external gear. The planet gear 3 is a 40 teeth external gear. The ring gear 5 is a 100 teeth internal gear. The ring gear 5 is fixed and the gear 2 is rotating at 50 rpm ccw (ccw=counterclockwise and cw=clockwise)
The arm 4 attached to the output shaft will rotate at (A) 10 rpm ccw (B) 10 rpm cw (C) 12 rpm cw (D) 12 rpm ccw
37. A forged steel link with uniform diameter of 30mm at the centre is subjected to an axial force that varies from 40kN in compression to 160kN in tension. The tensile (Su), yield (Sy) and corrected endurance (Se) strengths of the steel material are 600MPa, 420MPa and 240MPa respectively. The factor of safety against fatigue endurance as per Soderberg’s criterion is (A) 1.26 (B) 1.37 (C) 1.45 (D) 2.00
38. An automotive engine weighing 240kg is supported on four springs with linear characteristics. Each of the front two springs have a stiffness of 16MN/m while the stiffness of each rear spring is 32MN/m. The engine speed (in rpm), at which resonance is likely to occur, is (A) 6040 (B) 3020 (C) 1424 (D) 955
39. A vehicle suspension system consists of a spring and a damper. The stiffness of the spring is 3.6kN/m and the damping constant of the damper is 400Ns/m. If the mass is 50kg, then the damping factor (D) and damped natural frequency (fn), respectively, are (A) 0.471 and 1.19Hz (B) 0.471 and 7.48Hz (C) 0.666 and 1.35Hz (D) 0.666 and 8.50Hz
40. A frame of two arms of equal length L is shown in the adjacent figure. The flexural rigidity of each arm of the frame is EI. The vertical deflection at the point of application of load P is
(A) (B) (C) (D)
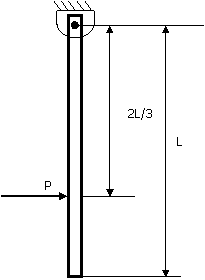
(A) -P (B) 0 (C) P/3 (D) 2P/3
42. Match the approaches given below to perform stated kinematics / dynamics analysis of machine. Analysis Approach P. Continuous relative rotation 1. D’ Alembert’s principle Q. Velocity and acceleration 2. Grubler’s criterion R. Mobility 3. Grashoff’s law S. Dynamic-static analysis 4. Kennedy’s theorem (A) P-1,Q-2,R-3,S-4 (B) P-3,Q-4,R-2,S-1 (C) P-2,Q-3,R-4,S-1 (D) P-4,Q-2,R-1,S-3
43. A company uses 2555 units of an item annually. Delivery lead time is 8 days. The recorder point (in number of units) to achieve optimum inventory is (A) 7 (B) 8 (C) 56 (D) 60
44. Consider the following Linear Programming Problem (LPP): Maximize z = 3x1 + 2x2 Subject to x1 £ 4 x2 £ 4 3x1 + 2x2 £ 18 x1 ³ 0, x2 ³ 0 (A) The LPP has a unique optimal solution (B) The LPP is infeasible (C) The LPP is unbounded (D) The LPP has multiple optimal solutions
45. Six jobs arrived in a sequence as given below:
Average flow time (in days) for the above jobs using Shortest Processing Time rule is (A) 20.83 (B) 23.16 (C) 125.00 (D) 139.00
46. Minimum shear strain in orthogonal turning with a cutting tool of zero rake angle is (A) 0.0 (B) 0.5 (C) 1.0 (D) 2.0
47. Electrochemical machining is performed to remove material from an iron surface of 20mm ´ 20mm under the following conditions: Inter electrode gap = 0.2mm Supply voltage DC = 12V Specific resistance of electrolyte = 2W cm Atomic weight of Iron = 55.85 Valency of Iron = 2 Faraday 's constant = 96540 Coulombs The material removal rate (in g/s) is (A) 0.3471 (B) 3.471 (C) 34.71 (D) 347.1
48. Match the following NC Code Definition P. M05 1. Absolute coordinate system Q. G01 2. Dwell R. G04 3. Spindle stop S. G90 4. Linear interpolation (A) P-2,Q-3,R-4,S-1 (B) P-3,Q-4,R-1,S-2 (C) P-3,Q-4,R-2,S-1 (D) P-4,Q-3,R-2,S-1
49. What are the upper and lower limits of the shaft represented by 60 f8? Use the following data: Diameter 60 lies in the diameter step of 50-80mm Fundamental tolerance unit, i, in mm=0.45D1/3 + 0.001D, where D is the representative size in mm; Tolerance value for IT8=25i. Fundamental deviation for ‘f’ shaft = -5.5D0.41 (A) Lower limit = 59.924mm, Upper Limit = 59.970mm (B) Lower limit = 59.954mm, Upper Limit = 60.000mm (C) Lower limit = 59.970mm, Upper Limit = 60.016mm (D) Lower limit = 60.000mm, Upper Limit = 60.046mm
50. Match the items in Column I and Column II. Column I Column II P. Metallic Chills 1. Support for the core Q. Metallic Chaplets 2. Reservoir of the molten metal R. Riser 3. Control cooling of critical sections S. Exothermic Padding 4. Progressive solidification (A) P-1,Q-3,R-2,S-4 (B) P-1,Q-4,R-2,S-3 (C) P-3,Q-4,R-2,S-1 (D) P-4,Q-1,R-2,S-3
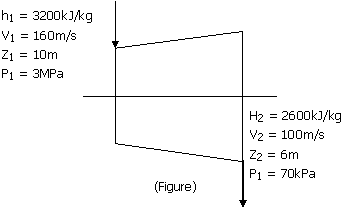
Common Data Questions: 51 & 52 The inlet and the outlet conditions of stream for an adiabatic steam turbine are as indicated in the notations are as usually followed
51. If mass flow rate of steam through the turbine is 20kg/s, the power output of the turbine (in MW) is (A) 12.157 (B) 12.941 (C) 168.001 (D) 168.785
52. Assume the above turbine to be part of a simple Rankine cycle. The density of water at the inlet to the pump is 1000kg/m3. Ignoring kinetic and potential energy effects, the specific work (in kJ/kg) supplied to the pump is (A) 0.293 (B) 0.351 (C) 2.930 (D) 3.510
Common Data Questions: 53 & 54 Radiative heat transfer is intended between the inner surfaces of two very large isothermal parallel metal plates. While the upper plate (designated as plate 1) is a black surface and is the warmer one being maintained at 727ºC, the lower plate (plate 2) is a diffuse and gray surface with an emissivity of 0.7 and is kept at 227ºC. Assume that the surfaces are sufficiently large to form a two-surface enclosure and steady state conditions to exist. Stefan Boltzmann constant is given as 5.67×10-8W/m2K4
53. The irradiation (in kW/m2) for the upper plate (plate 1) is (A) 2.5 (B) 3.6 (C) 17.0 (D) 19.5
54. If plate 1 is also a diffuse and gray surface with an emissivity value of 0.8, the net radiation heat exchange (in kW/m2) between plate 1 and plate 2 is (A) 17.0 (B) 19.0 (C) 23.0 (D) 31.7
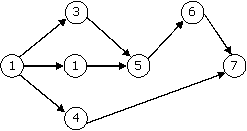
Common Data Questions: 55 & 56 Consider the following PERT network: The optimistic time, most likely time and pessimistic time of all the activities are given in the table below
55. The critical path duration of the network (in days) is (A) 11 (B) 14 (C) 17 (D) 18
56. The standard deviation of the critical path is (A) 0.33 (B) 0.55 (C) 0.77 (D) 1.66
Linked Answer Questions: Q.57 to Q.60 Carry Two Marks Each Statement for Linked Answer Questions: 57 & 58
In a machining experiment, tool life was found to vary with the cutting speed in the following manner:
57. The exponent (n) and constant (k) of the Taylor’s tool life equation are
(A) n = 0.5 and k= 540 (B) n = 1 and k= 4860 (C) n = −1 and k = 0.74 (D) n = −0.5 and k = 1.155
58. What is the percentage increase in tool life when the cutting speed is halved? (A) 50% (B) 200% (C) 300% (D) 400%
Statement for Linked Answer Questions: 59 & 60 A 20º full depth involute spur pinion of 4mm module and 21 teeth is to transmit 15kW at 960rpm. Its face width is 25mm. 59. The tangential force transmitted (in N) is (A) 3552 (B) 2611 (C) 1776 (D) 1305
60. Given that the tooth geometry factor is 0.32 and the combined effect of dynamic load and allied factors intensifying the stress is 1.5; the minimum allowable stress (in MPa) for the gear material is (A) 242.0 (B) 166.5 (C) 121.0 (D) 74.0 End of Question Paper |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||