|
1. Give i =  , the ratio , the ratio
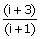 is
given by is
given by
(A) i (B) – 2 (C) – i + 2 (D) i + 1
|
|
2. The value
of "a" for which the following set of
equations
y + 2z = 0
2x + y + z = 0
ax + 2y = 0
have non-trivial solution, is
(A) 0 (B) 8 (C) – 2 (D) 3
|
|
3. The initial
condition for which the following equation
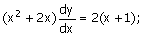 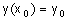
has infinitely many solutions, is
(A) y (x = 0) = 5 (B) y (x = 0) = 1 (C) y (x = 2) = 1 (D) y (x = –2) = 0
|
|
4. Give
that the Laplace transform of the function below over
a single period 0 < t < 2 is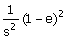 , the Laplace transform of the periodic
function over 0 < t < ∞ is , the Laplace transform of the periodic
function over 0 < t < ∞ is
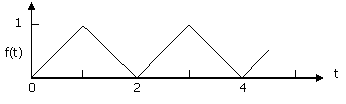
(A) 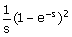 (B) (B) 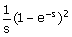 (C) (C) 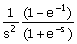 (D) (D) 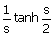
|
|
5. If TA and TB are the boiling points of pure A and
pure B respectively and TAB is
that of a non-homogeneous immiscible mixture of A and B, then
(A) TAB < TA and TB (B) TAB > TA and TB
(C) TA > TAB > TB (D) TB > TAB > TA
|
|
6. The state
of an ideal gas is changed from (T1, P1) to (T2,
P2) in a constant volume process. To calculate the change in enthalpy, Δh, ALL of the following
properties/variables are required.
(A) CV,
P1, P2 (B) CP, T1, T2
(C) CP,
T1, T2, P1, P2 (D) CV,
P1, P2, T1, T2
|
|
7. The change
in entropy of the system, ΔSsys, undergoing a cyclic
irreversible process is
(A) greater than 0 (C) less
than zero
(B) equal to zero (D) equal to the ΔSsurroundings
|
|
8. Parameters 'a' and 'b' in the van
der Waals and other cubic equations of state represent
(A) a
– molecular weight b – molecular polarity
(B) a – molecular
size b
– molecular attraction
(C) a – molecular
size b
– molecular speed
(D) a – molecular attraction b
– molecular size
|
|
9. If mi,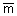 ,
miR, miE are molar, partial molar, residual
and excess properties respectively for a pure species "i", the mixture
property M of a binary non-ideal mixture of
components 1 and 2, is given by ,
miR, miE are molar, partial molar, residual
and excess properties respectively for a pure species "i", the mixture
property M of a binary non-ideal mixture of
components 1 and 2, is given by
(A) x1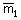 + x2
+ x2 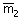 (B) x1 m1R + x2 (B) x1 m1R + x2 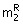
(C) x1 m1 + x2 m2 (D) x1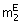 + x2
+ x2 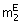
|
|
10. Consider a soap film bubble of
diameter D. If the
external pressure is Po and the
surface tension of the soap film is σ, the expression for the
pressure inside the bubble is
(A) P0 (B) 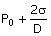 (C) (C) 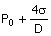 (D) (D) 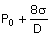
|
|
11. In Tyler series, the ratio of the aperture size
of a screen to that of the next smaller screen is
(A) 1/ √ 2 (B) √
2 (C) 1.5 (D) 2
|
|
12. Size reduction of coarse hard solids
using a crusher is accomplished by
(A) attrition (B) compression (C) cutting (D) impact
|
|
13. In constant pressure filtration, the
rate of filtration follows the relation
(v: filtrate volume, t : time, k and c : constants).
(A) 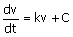 (B) (B) 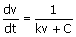 (C) (C) 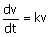 (D) (D) 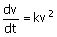
|
|
14. Sticky materials are transported by
(A) apron
conveyor (B) screw
conveyor
(C) belt
conveyor (D) hydraulic conveyor
|
|
15. The Grashof Number is
(A) thermal
diffusivity/mass diffusivity (B) inertial
force/surface tension force
(C) sensible
heat / latent heat (D) buoyancy
force / viscous force
|
|
16. An operator was told to control the
temperature of a reactor at 60°C. The
operator set the set-point of the temperature controller at 60. The scale actually indicated 0 to
100% of a temperature range of 0 to 200°C. This caused a runaway reaction by
over-pressurizing the vessel, which resulted in injury to the operator. The actual set-point temperature was
(A) 200°C (B) 60°C (C) 120°C (D) 100°C
|
|
17. Select the most appropriate pump
from Group 2 to handle each fluid flow given in Group 1,
Group
1 Group 2
P. Highly
viscous fluid flow (1)
piston pump
Q. Fluid
containing large amount of Abrasive
solids (2)
gear pump
(3) plunger pump
(4)
centrifugal pump
(A) P-(2),
Q-(1) (B) P-(2),
Q-(4)
(C) P-(3),
Q-(4) (B) P-(4), Q-(3)
|
|
18. A
cylindrical storage tank can have a self-supported conical roof,
(A) if
its diameter is less than 20 m
(B) if
its diameter is more than 50 m
(C) if
the thickness of the roof is more than that of the cylindrical shell
(D) whatever is the diameter
|
|
19. Which of the following is desirable
in gasoline but undesirable in kerosene?
(A) Aromatics (B) Mercaptans
(C) Naphthenic
Acid (D) Paraffins
|
|
20. In the Sulfite process for paper
manufacture, the 'cooking liquor' is
(A) Magnesium
bisulfite and sulfur dioxide in acid medium
(B) Magnesium
sulfite and magnesium dicarbonate
(C) Sodium
sulfite and magnesium sulfite
(D) Sodium
sulfite, sodium bisulfite and sulfur dioxide.
|
|
Q. 21 to 75 carry
two marks each.
|
|
21. If z = x + iy is
a complex number, where i = 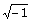 then
the derivative of z then
the derivative of z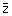 at 2
+ i is at 2
+ i is
(A) 0 (B) 2 (C) 4 (D) does
not exist
|
|
22. 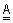 and
and 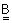 are two 3 x 3 matrix such that,
are two 3 x 3 matrix such that, 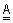 = =
 , ,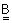 = =
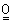 and and 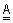 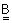 = =
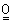 .
Then the rank of matrix .
Then the rank of matrix 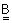 is is
(A) r = 2 (B) r < 3 (C) r ≤ 3 (D) r = 3
|
|
23. The solution of the following g
differential equation g
differential equation 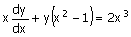 is is
(A) 0 (B) 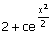 (C) c1x + c2 x2 (D) (C) c1x + c2 x2 (D) 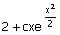
|
|
24. The
directional derivative of 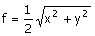 at
(1, 1) in the direction of at
(1, 1) in the direction of 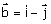 is is
(A) 0 (B) 1/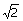 (C) (C) 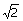 (D) 2 (D) 2
|
|
25. Evaluate the following integral (n
≠ 0)
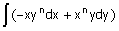
within
the area of a triangle with vertices (0, 0), (1, 0) and (1,1)
(counter-clockwise)
(A) 0 (B) 1/(n + 1) (C) 1/2 (D) n/2
|
|
26. The family of curves that is
orthogonal to xy = c is
(A) y = c1x (B) y = c1/x (C) y2 + x2 = c1 (D) y2 – x2 = c1
|
|
27. The Laplace transform of 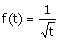 is is
(A) 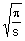 (B) (B) 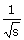 (C) (C) 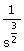 (D) does not exist (D) does not exist
|
|
28. The thickness of a conductive
coating in micrometers has a probability density function of 600 x--2 for 100 μm < x < 120 μm. The mean and the variance of the
coating thickness is
(A) 1
μm, 108.39 μm2 (B) 33.83
μm, 1 μm2
(C) 105 μm, 11 μm2 (D) 109.39
μm, 33.83 μm2
|
|
29. If the percent humidity of air (30
°C, total pressure 100 kPa) is 24 % and the saturation pressure of water
vapor at that temperature is 4 kPa, the percent relative humidity and the
absolute humidity of air are
(A) 25.2,
0.0062 (B) 25, 0.0035 (C) 20.7,
0.0055 (D) 18.2, 0.00
|
|
30. For
the two paths as shown in the figure, one reversible and one irreversible, to
change the state of the system from a to b,
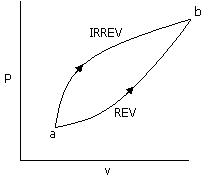
(A) ΔU, Q,
W are
same (B) ΔU, is same
(C) Q, W are
same (D) ΔU, Q, are
different.
|
|
31. For a pure substance, the Maxwell's
relation obtained from the fundamental property relation
du = Tdz
– Pdv is
(A) 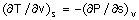 (B) (B) 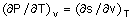
(C) 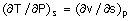 (D) (D) 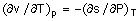 . .
|
|
32. Which of the following represents
the Carnot cycle (ideal engine)?
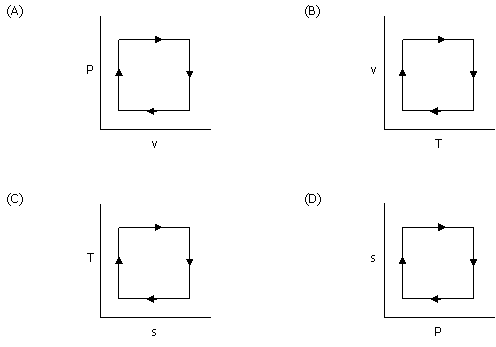
|
|
33. 2
kg of steam in a piston-cylinder device at 400 kPa and 175 °C undergoes a
mechanically reversible, isothermal compression to a final pressure such that
the steam becomes just saturated. What
is the work, W, required for the process.
Data:
T = 175°C, P = 400 kPa – v =
0.503 m3/kg, u = 2606 kJ/kg, s = 7.055 kJ/kg-K
T = 175°C, satd. vapor – v
= 0.216 m3/kg, u = 2579 kJ/kg, s = 6.622 kJ/kg-K
(A) 0
kJ (B) 230 kJ (C) 334
kJ (D) 388 kJ
|
|
34. Vapor phase hydration of C2H4 to ethanol by the following
reaction
C2H4 (g) + H2O
(g) ↔ C2H5 OH (g)
attains equilibrium at 400 K and 3
bar. The standard Gibbs
free energy change of reaction at these conditions is Δg° = 4000
J/mol. For 2 moles of an
equimolar feed of ethylene and steam, the equation in terms of the extent of reaction
ε (in mols) at equilibrium is
(A) 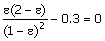 (B) (B) 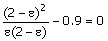
(C) 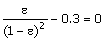 (D) (D) 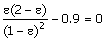
|
|
35. A pipeline system carries crude oil
of density 800 kg/m3. The
volumetric flow rate at point 1 is 0.28 m3/s. The cross sectional areas of the
branches 1, 2 and 3 are 0.012, 0.008 and 0.004 m2 respectively. All the three branches are in a
horizontal plane and the friction is negligible. If the pressures at the points 1 and
3 are 270 kPa and 240 kPa respectively, then the pressure at point 2 is
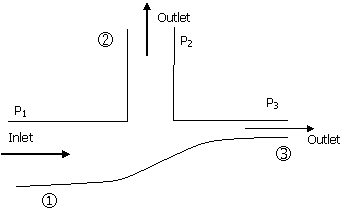
(A) 202
kPa
(B) 240
kPa
(C) 284
kPa
(D) 355
kPa
|
|
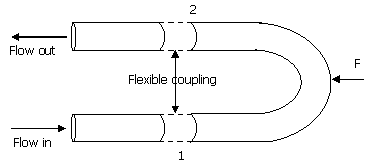
36. The figure shows the idealized view
of a return elbow or U bend, which is connected to two pipes by flexible
hoses that transmit no force. Water with density 1000 kg/m3 flows at velocity of 10 m/s through
the pipe, which has a uniform ID of 0.1m. The gauge pressure at points 1 and 2
are 304 kPa and 253 kPa respectively. The
horizontal force F required to keep the elbow in
position is
(A) 1574
N (B) 1970
N (C) 5942
N (D)
7533 N
|
|
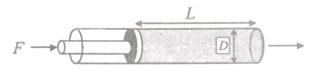
37. A tube of diameter D and length L is initially filled with a liquid of
density ρ and viscosity μ. It is then pushed out by the
application of a constant force F to the plunger as shown in the
figure. Assuming laminar
flow and pseudo steady state, the time required to expel one half of the
liquid out of the tube is
(A) 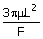 (B) (B) 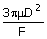 (C) (C) 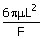 (D) (D) 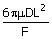
|
|
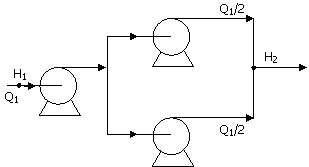
38. The figure shows a series-parallel
configuration of three identical centrifugal pumps. The head increase ΔH across a single such pump varies
with flowrate Q according to ΔH = a – bQ2. The
expression for the total head increase ΔH = H2 – H1 in terms of a and b and the total flowrate Q1 for this configuration is given
by
(A) 2a
- 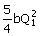
(B) 2a
- 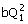
(C) 2a - 2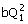
(D) a - 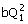
|
|
39. The
pressure differential across a venturimeter, inclined at 45° to the vertical
(as shown in the figure) is measured with the help of a manometer to estimate
the flowrate of a fluid flowing through it. If the density of the flowing fluid
is ρ and the
density of the manometer fluid is ρm,
the velocity of the fluid at the throat can be obtained from the expression
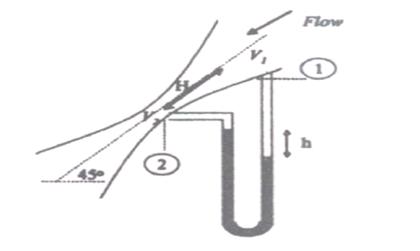
(A) 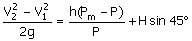 (B) (B) 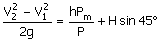
(C) 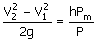 (D) (D) 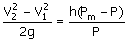
|
|
40. In the Stokes regime, the terminal
velocity of particles for centrifugal sedimentation is given by
Ut = ω2r (ρP - ρ) 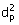 /18 μ /18 μ
where,
ω: angular
velocity; r : distance of the particle from the
axis of rotation;
ρp: density of the
particle; ρ : density of the
fluid; dP: diameter of the particle and μ : viscosity of the fluid.
In a Bowl centrifugal classifier
operating at 60 rpm with water (μ =
0.001 kg/m.s), the time taken for a particle (dp= 0.0001 m,
sp.gr = 2.5) in seconds to traverse a distance of 0.05 m from the liquid
surface is
(A) 4.8 (B) 5.8 (C) 6.8 (D) 7.8
|
|
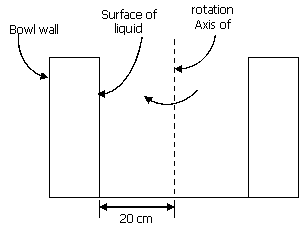
41. For the two long concentric
cylinders with surface areas A1 and A2, the view
factor F22 is given by
(A) 0
(B) 1 (C) 1
– A1/A2 (D) A1/A2
|
|
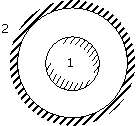
42. The composite wall of an oven
consists of three materials A, B and C. Under steady state operating conditions,
the outer surface temperature Tso is 20 °C, the inner surface
temperature Tsi is 600 °C and the oven air
temperature isT∞ =
800 °C. For the following
data
thermal
conductivities kA = 20 W/(m K) and kC = 50 W/m K), thickness LA = 0.3 m, LB = 0.15 m and LC = 0.15 m,
inner-wall heat transfer coefficient
h = 25 W/m2 K),
the thermal conductivity kB W/(mK) of the material B, is
calculated as
(A) 35 (B) 1.53
(C) 0.66
(D) 0.03
|
|
43. Water enters a thin walled tube (L = 1 m, D = 3 mm) at an inlet temperature of
97°C and mass flow rate 0.015 kg/s. The
tube wall is maintained at a constant temperature of 27°C. Given the following data for water.
Density, ρ = 1000
kg/m3
Viscosity, μ = 489
10-6 Ns/m2
Specific heat Cp = 4184
J/kg/k
Inside heat transfer coefficient h =
12978 W/ (m2 K),
The outlet temperature of water
in °C is,
(A) 28 (B) 37 (C) 62 (D) 96
|
|
44. A hot fluid entering a well-stirred
vessel is cooled by feeding cold water through a jacket around the vessel.
Assume the jacket is well-mixed. For the following data,
mass
flowrates of the hot fluid = 0.25 kg/s
mass flow rate of cold water = 0.4 kg/s
specific heats of
oil = 6000 J/kgK
specific heat of cold water = 4184
J/kgK
the inlet and exit temperature of
the hot fluid is 150°C and 100°C respectively.
inlet
temperature of cold water = 20
°C
the overall hat transfer coefficient
is 500 W/m2K.
the
heat transfer area in m2, is
(A) 1.82 B) 2.1 (C) 3 (D) 4.26
|
|
45. Consider a liquid stored in a
container exposed to its saturated vapor at constant temperature Tsat. The bottom surface of the container
is maintained at a constant temperature Ts < Tsat while its side walls are
insulated. The thermal
conductivity k1 of
the liquid, its latent heat of vapourisation λ and density ρ1 are
known. Assuming a linear
temperature distribution in the liquid, the expression for the growth of the
liquid layer δ as a function of time t is
given by
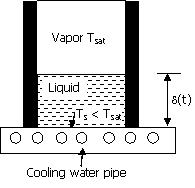
(A) 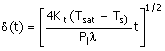 (B)
(B) 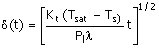
(C) 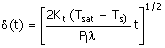 (D) (D) 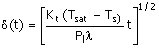
|
|
46. The following list of options P, Q,
R and S are some of the important considerations in the design of a shell and
tube heat exchanger.
(P) square
pitch permits the use of more tubes in a given shell diameter
(Q) the
tube side clearance should not be less than one fourth of the tube diameter
(R) baffle
spacing is not greater than the diameter of the shell or less than one-fifth
of the shell diameter
(S) The
pressure drop on the tube side is less than 10 psi.
Pick
out the correct combination of 'TRUE' statements from the following:
(A) P,
Q and R (B) Q, R and S
(C) R,
S and P (D) P, Q, S and S
|
|
47. The following figure depicts steady
one-dimensional diffusion of water vapour from the surface of water taken in
a conical flask at room temperature. Derive
the governing equation for determining the concentration profile of water
vapour in the gas medium. Neglect
change of level of water due to condensation. The temperatures of the gas and the
liquid media are identical and constant.

(A) 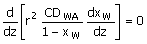 (B) (B)
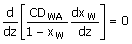
(C) 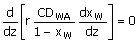 (D) (D) 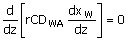
|
|
48. In a distillation operation, it is
desired to have a very high purity bottom product. Initially, a kettle-type reboiler is
used at the bottom of the column and the following analytical equation is
used to obtain the equilibrium trays in the exhausting section of the column
Np
- m + 1 = 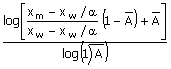
where xm is the composition of the liquid
leaving tray m. Tray m is the last
equilibrium tray obtained by a McCabe Thiele graph of the exhausting
section. If the
kettle-type reboiler is replaced by a thermo-syphon reboiler, the analytical
equation, for the exhausting section will be
(A) Np -
m + 1 = 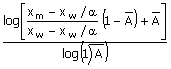 (B)
Np + 1 = (B)
Np + 1 = 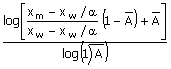
(C) Np
- m = 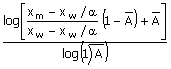 (D)
Np - m + 2 = (D)
Np - m + 2 = 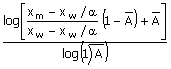
|
|
49. A 50 cm X 50 cm X 1 cm flat wet
sheet weighing 2 kg initially was dried from both the sides under constant
drying rate period. It
took 1000 secs for the weight of the sheet to reduce to 1.75 kg. Another 1m X
1m X 1cm flat sheet is to be dried from one side only. Under the same drying rate and other
conditions, time required for drying (in secs) from initial weight of 4 kg to
3 kg is
(A) 1000 (B) 1500 (C) 2000 (D) 2500
|
|
50. It is desired to reduce the
concentration of pyridine in 500 kg of aqueous solution from 20 weight
percent to 5 wt percent in a single batch extraction using chloro- benzene as
solvent. Equilibrium compositions (end points of the tie line) in terms of
weight percent of pyridine-water-chlorobenzene are (5, 95, 0) and (11, 0,
89).
The amount of pure solvent required
in kg for the operation is
(A) 607 (B) 639
(C) 931 (D) 1501
|
|
51. Benzene in an air-benzene mixture is
to be reduced from 5.2 mol% in the feed to 0.5 mol% by contacting with wash
oil in a multistage countercurrent gas absorber. The inlet flowrate of air- benzene
mixture is 10 mol/s while benzene free wash oil comes in at 9.5 mol/s. If the equilibrium curve is given as
Y* = X, where Y* and X are equilibrium mole ratios of benzene in air and
benzene in oil, the number of equilibrium stages required to achieve the
above separation is

(A) 12 (B) 10
(C) 8 (D) 6
|
|
52. A well-stirred reaction vessel is
operated as a semi-batch reactor in which it is proposed to conduct a liquid
phase first order reaction of the type A
→ B. The reactor is fed with the reactant A at a constant rate of 1 liter/min
having feed concentration equal to 1 mol/liter. The reactor is initially
empty. Given k = 1 min-1, the conversion
of reactant A based on
moles of A fed at t = 2 min is
(A) 0.136 (B) 0.43 (C) 0.57 (D) 0.864
|
|
53. A liquid phase exothermic first
order reaction is being conducted in a batch reactor under isothermal
conditions by removing heat generated in the reactor with the help of cooling
water. The cooling water
flows at a very high rate through a coil immersed in the reactor such that
there is negligible rise in its temperature from inlet to outlet of the
coil. If the rate
constant is given as k,
heat of reaction ( – ΔH ),
volume of the reactor, V,
initial concentration asCAO, overall heat transfer
coefficient, U, heat
transfer area of the coil is equal to A,
the required cooling water inlet temperature, Tci is given by the following equation :
(A) Tci
= T - 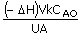 (B) Tci = T - (B) Tci = T - 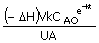
(C) Tci
= T - 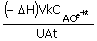 (D) Tci = T - (D) Tci = T - 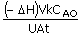
|
|
54. The following liquid phase reaction
is taking place in an isothermal CSTR
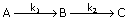
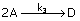
Reaction mechanism is same as the
stoichiometry given above. Given k1 = 1 min-1; k2 = 1 min-1; k3 = 0.5 lit/(mol)(min); CAO = 10 mol/litre, CBO = 0 mol/litre and CB = 10 mol/litre, the
solution for F/V (flow rate/reactor volume in min-1)
yields
(A) 6.7 (B) 6
and 0.5 (C) 2
and 4/3 (D) 8
|
|
55. A pulse of concentrated KC1 solution
is introduced as tracer into the fluid entering a reaction vessel having
volume equal to 1 m3 and
flow rate equal to 1 m3/min. The concentration of tracer measured
in the fluid leaving the vessel is shown in the figure given below. The flow model parameters that fit
the measured RTD in terms of one or all of the following mixing elements, namely,
volume of plug flow reactor, Vp,
mixed flow volume, Vm,
and dead space,Vd, are
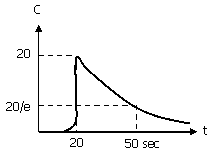
(A) Vp =
1/6 m3, Vm = 1/2 m3, Vd = 1/3 m3
(B) Vp = Vm = Vd =
1/3 m3
(C) Vp = 1/3 m3, Vm = 1/2 m3, Vd = 1/6 m3
(D) Vm=
5/6 m3, Vd = 1/6 m3 |
|
56. The first order reaction of A to R is run in an experimental mixed flow
reactor. Find the role
played by pore diffusion in the run given below. CAO is 100 and W is fixed. Agitation rate was found to have no
effect on conversion.
dp FAO
XA
4
2
0.8
6
4
0.4
(A) strong
pore diffusion control
(B) diffusion free
(C) intermediate
role by pore diffusion
(D) external
mass transfer
|
|
57. A packed bed reactor converts A to R by first order reaction with 9 mm
pellets in strong pore diffusion regime to 63.2% level. If 18 mm pellets are used what is
the conversion.
(A) 0.39 (B) 0.61 (C) 0.632
(D) 0.865
|
|
58. The following rate-concentration
data are calculated from experiment. Find
the activation energy temperature (E/R) of the first order reaction.
dp CA
–rA T
1
20
1
480
2
40
2
480
2
40
3
500
(A) 2432.8 (B) 4865.6 (C) 9731.2 (D) 13183.3 |
|
59. Determine the level of CAO
(high, low, intermediate), temperature profile
(high, low, increasing, decreasing), which will favor the formation of the
desired product indicated in the reaction scheme given below.
n1 E1
n2 E2
n3 E3
2 25 1 35
3
45
(A) High CAO, increasing T, plug flow reactor
(B) Low CAO, increasing T,
plug flow reactor
(C) High CAO, decreasing T,
mixed flow reactor
(D) High CAO, decreasing T,
plug flow reactor
|
|
60. The dynamic model for a mixing tank
open to atmosphere at its top as shown below is to be written. The objective of mixing is to cool
the hot water stream entering the tank at a flow rate q2 and feed temperature of Ts with a cold water food stream
entering the tank at a flow rate q1 and feed temperature of T0. A water stream is drawn from the
tank bottom at a flow rate of q4 by
a pump and the level in the tank is proposed to be controlled by drawing
another water stream at a flow rate q3. Neglect evaporation and other heat
losses from the tank.
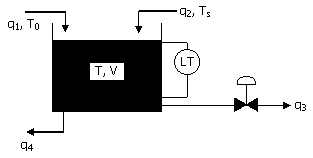
(A) 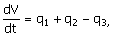 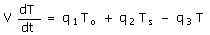
(B) 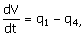 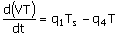
(C) 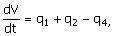 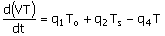
(D) 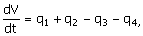 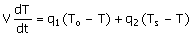
|
|
61. Match the transfer functions with
the responses to a unit step input shown in the figure.
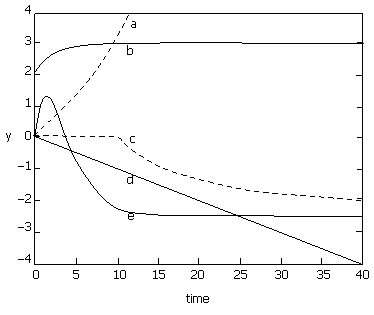
i. 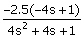
ii. 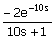
iii. 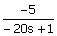
iv. 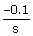
v. 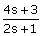
(A) i-e, ii-c, iii-a, iv-d, v-b
(B) i-a, ii-b, iii-c, iv-d, v-e
(C) i-b, ii-a, iii-c, iv-e, v-d
(D) i-e, ii-a, iii-c, iv-b, v-d
|
|
62. Consider
the following instrumentation diagram for a chemical reactor. Csp represents a concentration set
point.
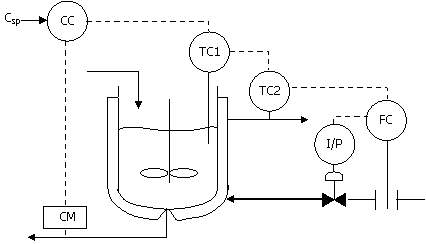
Match the items in group 1
with the corresponding items given in column B.
Column A Column B
P) control
strategy 1)
feed forward control
Q) primary control variable 2) cascade control
R) slowest
controller 3)
concentration in the reactor
S) fastest
controller 4)
reactor temperature
5) jacket temperature
6)
concentration controller
7)
reactor temperature controller
8)
jacket temperature controller
9)
flow controller
10)
selective control
(A) P-2,
Q-3, R-6,
S-9 (B) P-1, Q-4, R-8,
S-7
(C) P-10,
Q-7, R-9,
S-6 (D) P-1, Q-8, R-5,
S-9
|
|
63. The first two rows of Routh's
tabulation of a third order equation are
s3 2 2
s3 4 4
Select the
correct answer from the following choices:
(A) The
equation has one root in the right half s-plane
(B) The
equation has two roots on the j axis at s = j and – j. The third root is in the left half plane.
(C) The
equation has two roots on the j axis at s = 2j and s = –2j. The third root is in the left half
plane.
(D) The
equation has two roots on the j axis at s = 2j and s = –2j. The third root is in the right half
plane.
|
|
64. Given the following statements
listed from P to T, select the correct combination of TRUE statements from the choices that
follow this list.
P) Plate columns are
preferred when the operation involves liquids containing suspended solids.
Q) Packed towers are preferred
if the liquids have a large foaming tendency.
R) The pressure drop through
packed towers is more than the pressure drop through plate columns
designed for the same duty.
S) Packed columns are
preferred when large temperature changes are involved in distillation operations.
T) Packed towers are cheaper
than plate towers if highly corrosive fluids must be handled.
(A) T, S, P (B) P. Q. T (C) S, R, T (D) R, Q, S
|
|
65. A pump has an installed cost of Rs.
40,000 and a 10-year estimated life. The
salvage value of the pump is zero at the end of 10 years. The pump value (in rupees) after
depreciation y the double declining balance method, at the end of 6 years
is
(A) 4295 (B) 10486 (C) 21257 (D) 37600
|
|
66. In a double pipe heat exchanger the
ID and OD of the inner pipe are 4 cm and 5 cm respectively. The ID of the outer pipe is 10 cm
with a wall thickness of 1 cm. Then
the equivalent diameters (in cm) of the annulus for heat transfer and
pressure drop respectively are
(A) 15,
5 (B) 21,
6 (C) 6,
19 (D) 15, 21
|
|
67. Match the chemicals in Group 1 with
their function in Group 2.
Group
1 Group 2
P.
styrene 1)
buffer
Q. tert-dodecyl
mercaptan 2)
catalyst
R. potassium
pyrophosphate 3)
modifier
4)
monomer
(A) P-1,
Q-4, R-4, (B) P-4,
Q-1, R-2,
(C) P-4,
Q-1, R-3, (D) P-4,
Q-3, R-1,
|
|
68. Match the product in Group 1 with
its application in the industries of Group 2
Group
1 Group 2
P.
lithium stearate 1)
cosmetics
Q.
magnesium
stearate 2) paper
R. aluminium
sulphate 3) dry cleaning
(A) P-2,
Q-3, R-1, (B) P-3,
Q-4, R-2,
(C) P-4,
Q-2, R-3, (D) P-4,
Q-1, R-2,
|
|
69. Match the synthetic fibres in Group
1 with their classification in Group 2.
Group
1 Group
2
P.
Rayon 1)
polyamide
Q.
Orlon 2)
polyester
R.
Dacron 3)
cellulose
(A) P-2, Q-3,
R-1, (B) P-3, Q-4, R-2,
(C) P-3, Q-1,
R-3, (D) P-3, Q-3, R-4,
|
|
70. Match the Petrochemical derivative
in Group 1 with the raw materials in Group 2.
Group
1 Group 2
P.
acrylonitrile 1)
methane
Q.
ammonia 2)
ethane
R.
dodecene 3)
ethylene
4)
propylene
(A) P-1,
Q-2, R-1, (B) P-2,
Q-1, R-2,
(C) P-3,
Q-4, R-3, (D) P-4,
Q-1, R-4,
|
|
COMMON DATA QUESTIONS
Common Data for
Questions 71, 72, 73:
|
|
71. A cascade control system for
pressure control is shown in the figure given below. The pressure transmitter has a range
of 0 to 6 bar (g) and the flow transmitter range is 0 to 81 nm3/hr. The normal flow rate through the
valve is 32.4 nm3/hr corresponding to the value of set point for
pressure = 1 bar (g) and to give the flow, the valve must be 40%
opened. The control valve
has linear characteristics and is fail–open (air to close). Error, set point and control
variable are expressed in percentage transmitter output (% TO). Proportional gain is expressed in
the units of % controller output (CO/% TO).
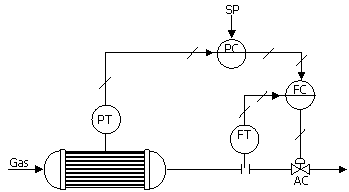
The types
of action for the two controllers are
(A) direct
acting for the pressure control and direct acting for the flow control
(B) indirect
acting for the pressure control and indirect acting for the flow control
(C) direct
acting for the pressure control and indirect acting for the flow control
(D) indirect
acting for the pressure control and direct acting for the flow control
|
|
72. The bias values for the two
controllers, so that no offset occurs in either controller are
(A) Pressure
controller: 40%; Flow controller: 60%
(B) Pressure
controller: 33%; Flow controller: 67%
(C) Pressure
controller: 67%; Flow controller: 33%
(D) Pressure
controller: 60%; Flow
controller: 40%
|
|
73. Given that the actual tank pressure
is 4 bar(g) and a proportional controller is employed for pressure control,
the proportional band setting of the pressure controller required to obtain a
set point to the flow controller equal to 54 nm3/hr is
(A) 50% (B) 100% (C) 150% (D) 187%
|
|
Common Data for
Questions 74, 75:
|
|
74. The following liquid phase reaction
is taking place in an isothermal batch reactor
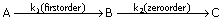
Feed concentration = 1 mol/litre
The time at which the concentration
of B will reach its maximum value is
given by
(A) t = 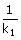 In In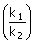 (B) t
= (B) t
= 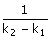 In In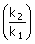
(C) t
= 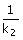 In In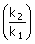 (D) t = (D) t = 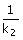 In In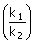 |
|
75. The time at which the concentration
of B will become zero is given by the following equation:
(A) 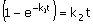 (B) t
= ¥ (B) t
= ¥
(C) t
= 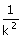 (D) t
= (D) t
= 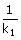
|
|
Linked Answer
Questions: Q. 76 to Q. 85 carry two marks each.
Statement for
Linked Answer Questions 76 & 77:
|
|
76. A methanol-water vapor liquid system
is at equilibrium at 60°C and 60 kPa. The
mole fraction of methanol in liquid is 0.5 and in vapor is 0.8. Vapor pressure of methanol and water
at 60°C are 85 kPa and 20 kPa respectively. Assuming vapor phase to be
an ideal gas mixture, what is the activity coefficient of water in the liquid
phase?
(A) 0.3
(B) 1.2 (C) 1.6 (D) 7.5
|
|
77. What is the excess Gibbs free energy
(gE, in J/mol) of the liquid mixture?
(A) 9.7
(B) 388 (C) 422 (D) 3227
|
|
Statement for
Linked Answer Questions 78 & 79:
78. A simplified flowsheet is shown in
the figure for production of ethanol from ethylene. The conversion of ethylene in the
reactor is 30% and the scrubber following the reactor completely separates
ethylene (as top stream) and ethanol and water as bottoms. The last (distillation) column gives
an ethanol-water azeotrope (90 mol% ethanol) as the final product and water
as waste. The recycle to
purge ratio is 34.
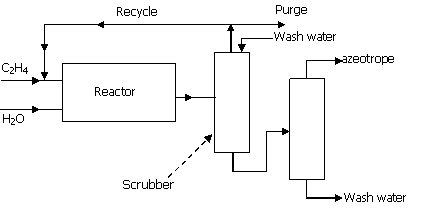
The
reaction is: C2H4 (g) + H2O (g) → C2H5OH (g)
For an azeotrope product rate of 500
mols/hr, the recycle gas flowrate in mols/hr is
(A) 30
(B) 420
(C) 1020 (D) 1500
|
|
79. For the same process, if fresh H2O
feed to the reactor is 600 mol/hr and wash water for scrubbing is 20% of the
condensables coming out of the reactor, the water flowrate in mols/hr from
the distillation column as bottoms is
(A) 170
(B) 220 (C) 270 (D) 430
|
|
Statement for
Linked Answer Questions 80 & 81:
|
|
80. 44 kg of C3H8 is burnt with 1160 kg of air (Mol.
Wt. = 29) to produce 88 kg of CO2 and 14 kg of CO
C3H8 + 5 O2 = 3 CO2 + 4 H2O
What is
the percent excess air used?
(A) 55
(B) 60
(C) 65
(D) 68
|
|
81. What is
the % carbon burnt?
(A) 63.3 (B) 73.3 (C) 83.3 (D) 93.3
|
|
Statement for
Linked Answer Questions 82 & 83:
82. A perfectly insulated cylinder of
volume 0.6 m3 is
initially divided into two parts by a thin, frictionless piston, as shown in
the figure. The smaller
part of volume 0.2 m3 has
ideal gas at 6 bar pressure and 100°C. The other part is evacuated.
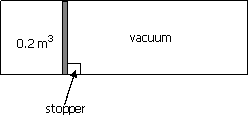
At certain
instant of time t, the stopper is removed and the piston moves out freely to
the other end. The final
temperature is
(A) –140°C
(B) –33°C
(C) 33°C (D) 100°C
|
|
83. The cylinder insulation is now
removed and the piston is pushed back to restore the system to its initial
state. If this is to be
achieved only by doing work on the system (no heat addition, only heat
removal allowed), what is the minimum work required?
(A) 3.4
kJ (B) 107 kJ (C) 132 kJ (D) 240 kJ
|
|
Statement for
Linked Answer Questions 84 & 85:
84. A fluidized bed (0.5m dia, 0.5m
high) of spherical particles (diameter = 2000 μm, specific gravity =
2.5) uses water as the medium. The
porosity of the bed is 0.4. The Ergun eqn. For the system is
ΔP/L = 4 x 105 Umf + 1 x 107 Umf2
(Sl unit, Umf in
m/s).
ΔP/L (SI unit) at minimum
fluidization condition is
(g = 9.8 m/sec2).
(A) 900
(B) 8820 (C) 12400 (D) 17640
|
|
85. The minimum fluidization velocity
(mm/sec) is
(A) 12.8 (B) 15.8 (C) 24.8 (D) 28.8
|